With over a decade of experience in website promotion and SEO (since 2007), I've encountered the issue of link farm sites numerous times.
A link farm is a cluster of sites that link to each other to make it look like they’re gaining backlinks naturally, just to trick search engines into ranking them higher.
As the term suggests, link farming is a pretty manipulative SEO move — but in my experience, around 90% of link-building agencies still offer links from backlink farms.
That’s why knowing how to tell sketchy platforms from real business sites is a must — especially if link-building is something you regularly outsource.
To help you with that, in this post, I’ll cover:
- What is a link farm
- Why people still buy from link farms
- How to spot a link farm (examples inside)
- Backlink farm alternative that works
- FAQ on link farming
What is a Link Farm?
A link farm is a ring of websites that may look unrelated at first but are actually owned by the same person.
The idea is simple: each site links to the others to inflate their backlink count and create a false sense of authority and trustworthiness.
Whenever a new site is added to the backlink farm, all the existing ones link to it — giving it an instant boost. In return, the newcomer joins the network, linking back to support the rest and any future sites.
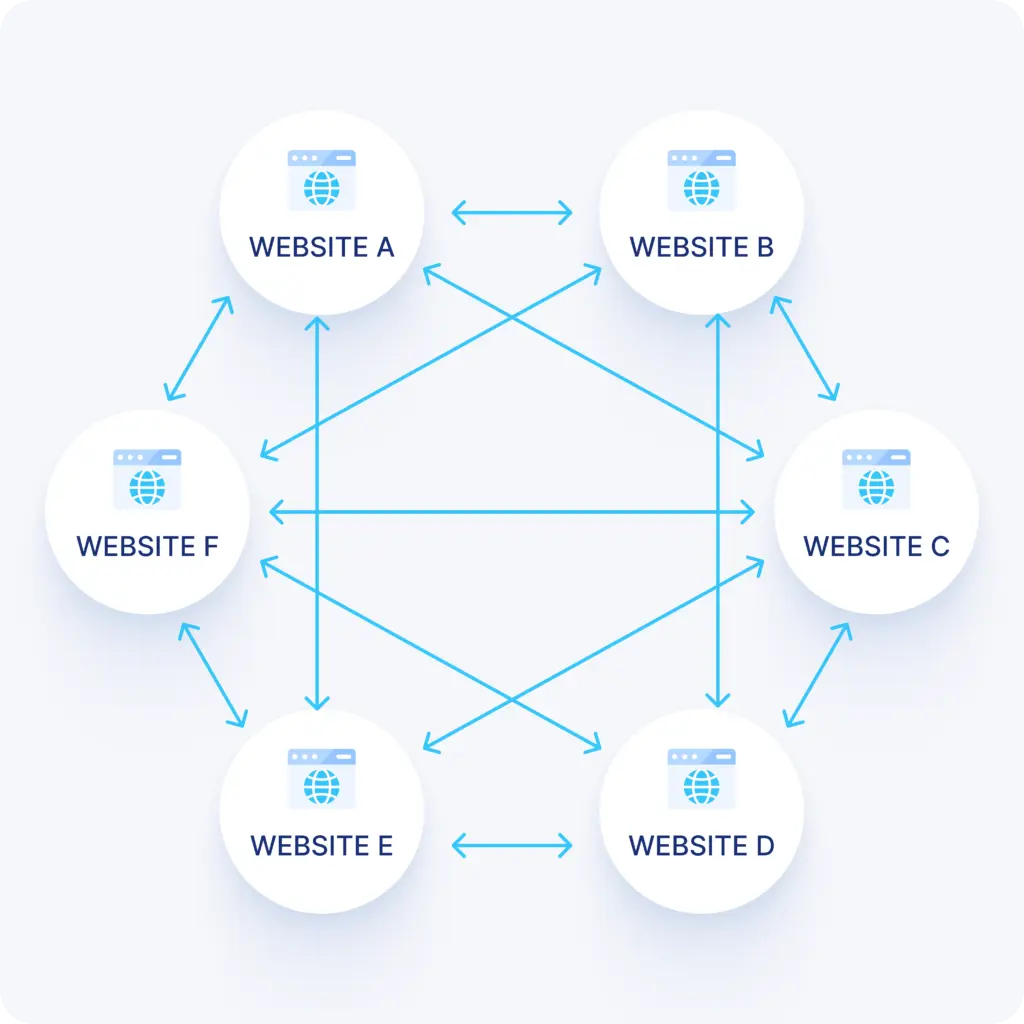
Sadly, in 2025, link farms still thrive — pumping out fake links that only help themselves. Local SEO takes the biggest hit, as businesses get trapped, lose trust, and give up on link building altogether.
For example, we recently had a client who spent $50K a year on backlinks — but saw no improvement in search visibility. In fact, their SEO performance actually got worse.
The image below (from Ahrefs) shows the links their contractor was building for them.
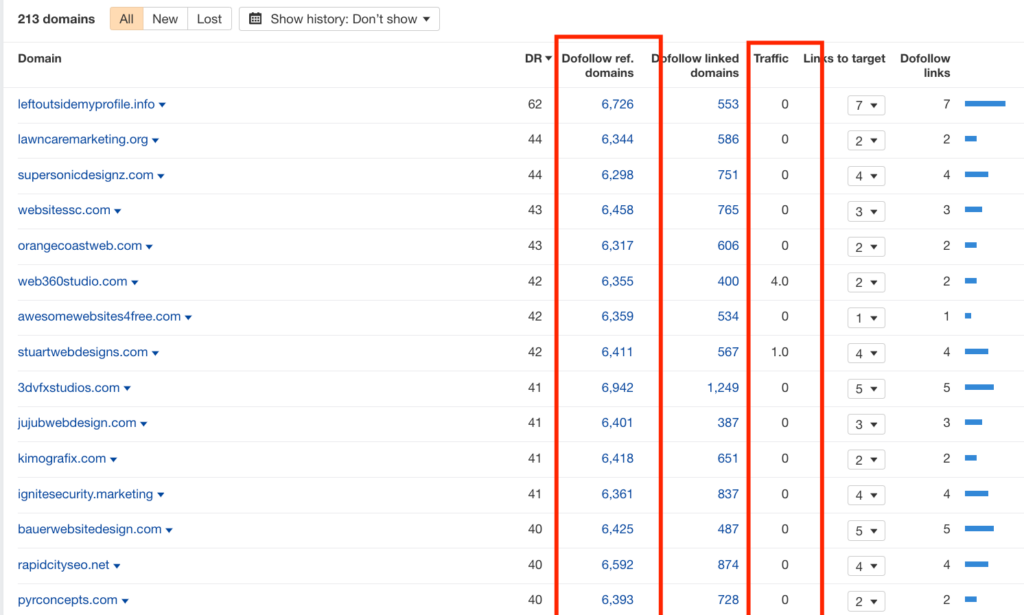
All the classic signs of an artificial blog network are clear: matching referring domains, similar Domain Ratings (DR), and zero traffic.
And that’s only scratching the surface 😱
Modern link farming has really gone pro — almost impossible to detect unless you’re in the know. Even online tools designed to spot link farms can be unreliable.
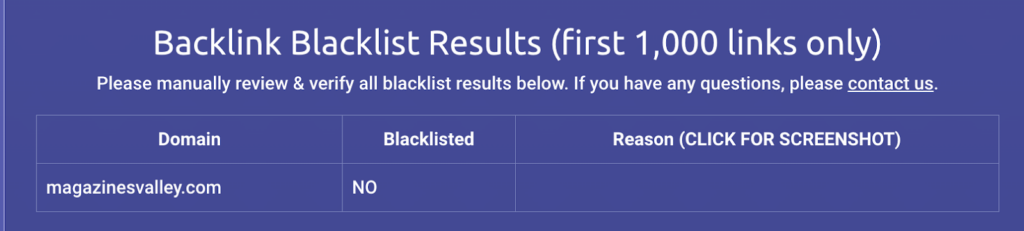
Take Matthew Woodward’s tool, for example — it features a blacklist of sites notorious for selling backlinks.
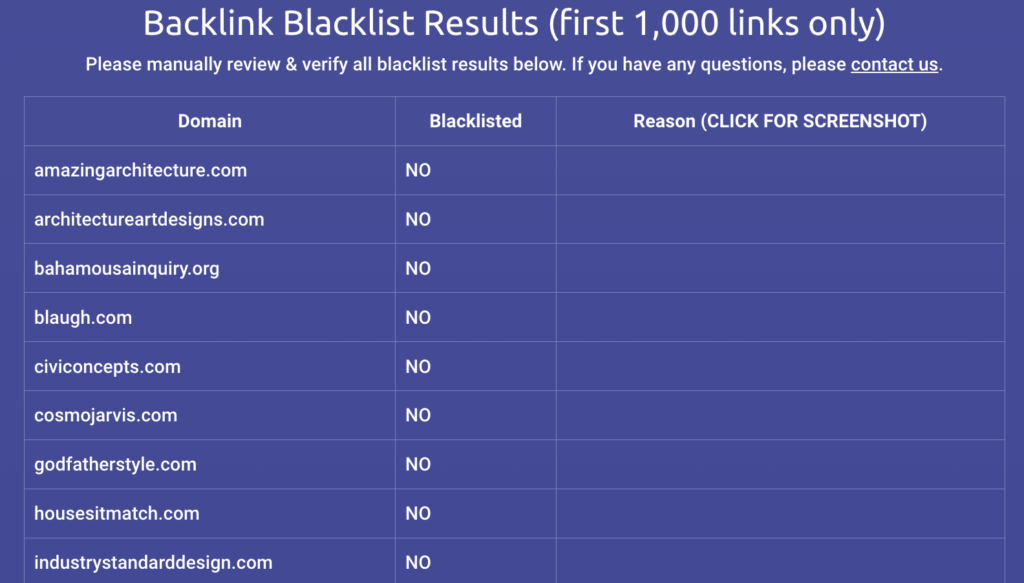
I decided to review one of the monthly reports that the client had ordered from a well-known link-building service before engaging with us.
$5,000 a month for 20 sites — that’s $250 per link, according to the client’s report.
Interestingly, none of the reported sites made it onto the blacklist.
Also, 3 out of the 20 sites were no longer accessible, even though it's been only 6 months since links from these sites were posted to the client's site.
💡Pro-tip! This usually happens because link farm owners stop renewing their domains if they get banned and deindexed by Google.
For more proof, let’s examine one of the domains in detail — magazinesvalley.com.
Here’s the “quality” site in question:
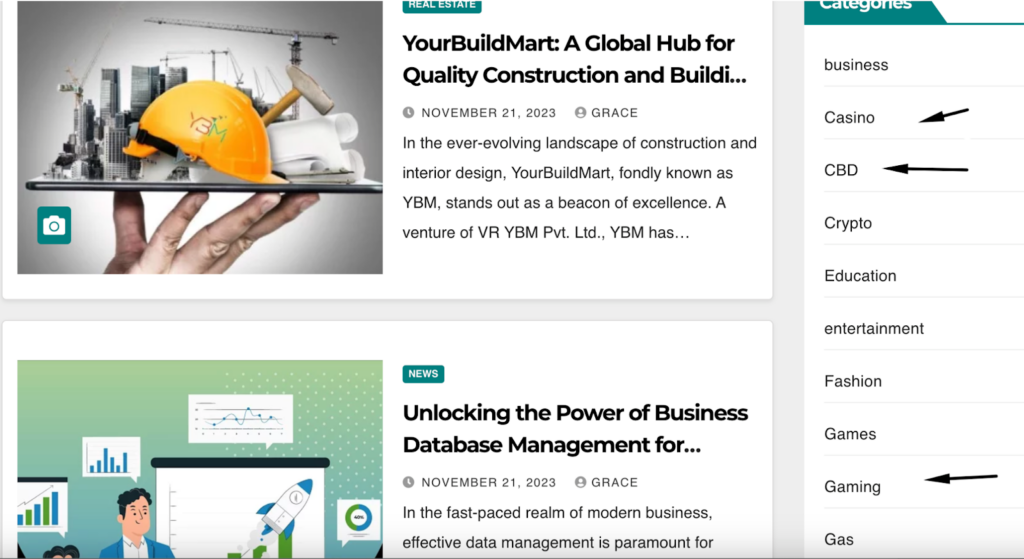
The site obviously operates as a link-selling platform, with numerous catch-all categories and sections filled with promotional articles on various topics — all designed specifically for buying links.
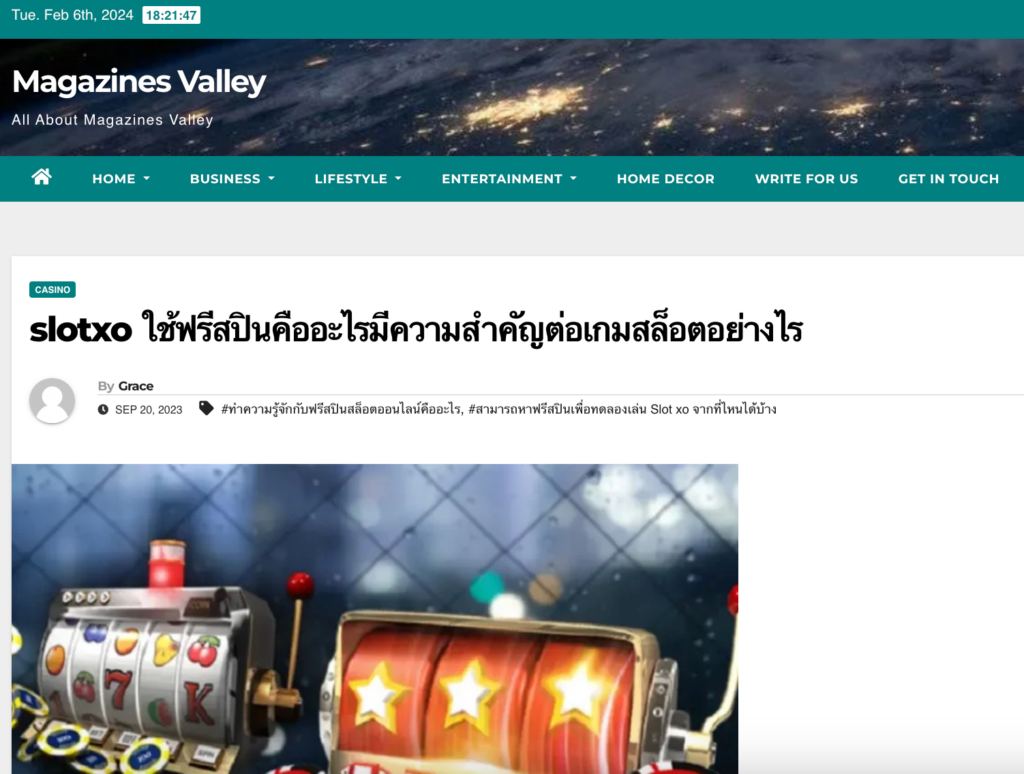
Check out one of these “articles” — pure casino advertising!
👌Wise Move! To spot a link farm fast, open Ahrefs’ Outgoing Anchors report and analyze the anchor texts of the links in question.
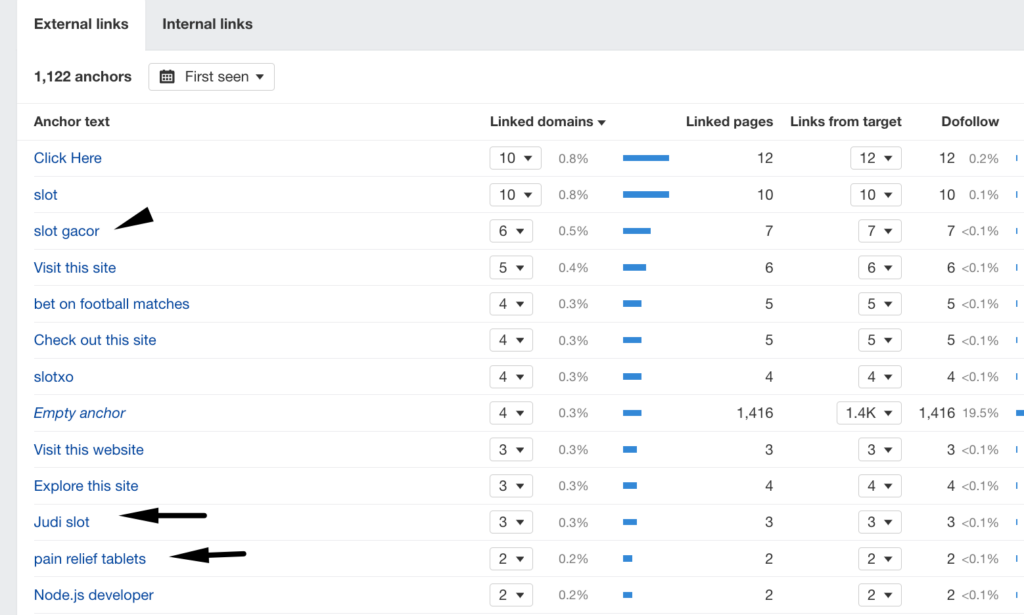
As the report reveals, links span diverse niches, including questionable and illegal ones, meaning the site accepts all sorts of placements without moderation.
If you don’t have Ahrefs or can’t access the outbound links report (often blocked by webmasters to hide outgoing links), you can try an alternative — search on Google using “site: magazinesvalley.com” operator.
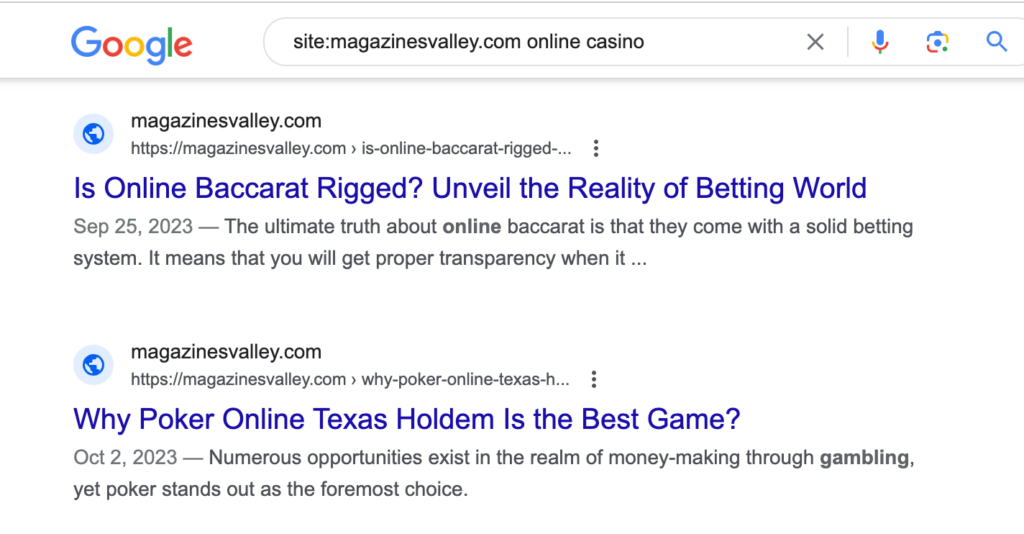
💡Pro-tip! When search results show links to gray and illegal niches, it’s a strong sign of a backlink farm.
Why People Still Buy From Link Farms?
First off, earning links is a grind in any niche.
But in high-stakes ones like legal services, it’s survival of the fittest — a single strong backlink can drive serious traffic and land clients worth thousands.
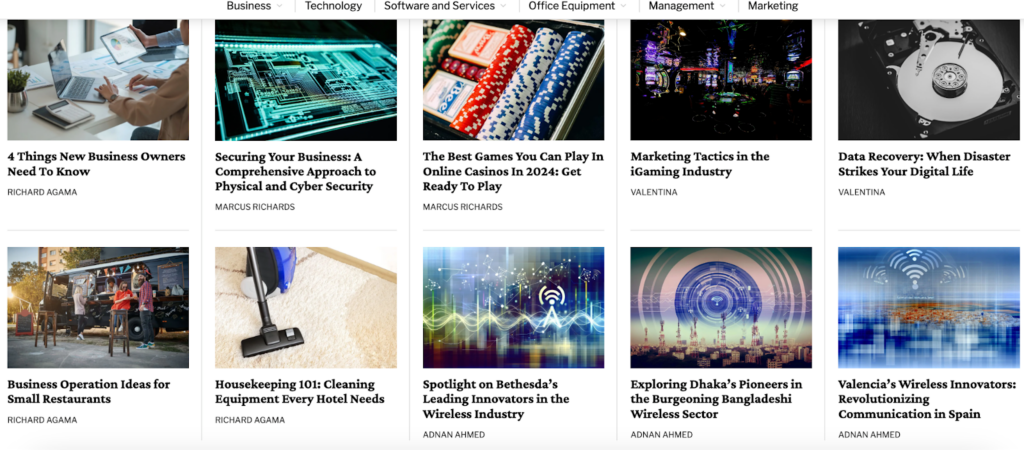
Not to mention the fierce link demand in software development outsourcing (see our case studies).
Budget constraints are another big reason why people fall into the trap of link farming. Hundreds of low-cost links may seem like a smart budget move — but that’s where quantity starts to trump quality.
Finally, plenty still don’t get the mere concept of link quality. “Why shell out $1,000 for a single DR 90 link when I can land 20 DR 70 links at just $50 a pop?” More links, less money…Zero clue about context or value, though 😕
💡Pro-tip! To see why context makes all the difference in link quality, read my post on forum link-building.
Circling back to the cost vs. quality dilemma we often see with clients, here’s an example:
Our manager told a client that a package of 5 links costs $1,750 ($350 per link), while 20 links go for $6,000 ($300 each).
Understandably, the client worried that the higher price per link might strain their budget.
This mindset is exactly what drives poor link-building decisions.
People assume 10 links beat one, and 1,000 beat 100.
As long as links remain an important ranking factor, link farm sellers will always have buyers.
Platforms like Fiverr are packed with cheap offers — and link farmers are quick to cash in.
How To Identify a Link Farm?
Link farms love to play dress-up, but the mask slips fast if you know the signs.
Check this list — if two or more boxes get ticked, you’re staring down a backlink farm.
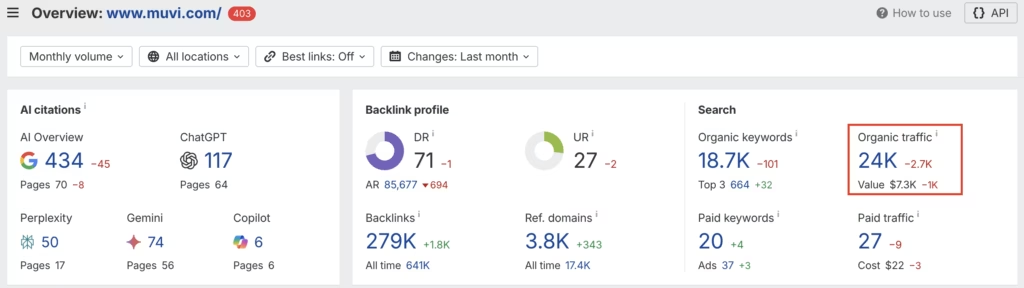
1. Organic traffic vs. traffic value
When a site has great organic traffic but no value behind it, something doesn’t add up.
🤔 Why it matters
Real sites targeting commercial or decision-driven queries tend to show solid traffic-value alignment. With link farms, traffic may be there — but it's mostly worthless.
👀 What link farms do
Link farms trade genuine traffic for inflated stats, all to fool SEO tools and profit off clueless buyers.
🔍 How to check
Look at the Organic Traffic vs. Traffic Value in Ahrefs or similar tools. Good traffic with little value usually means the site lacks real authority and user trust.
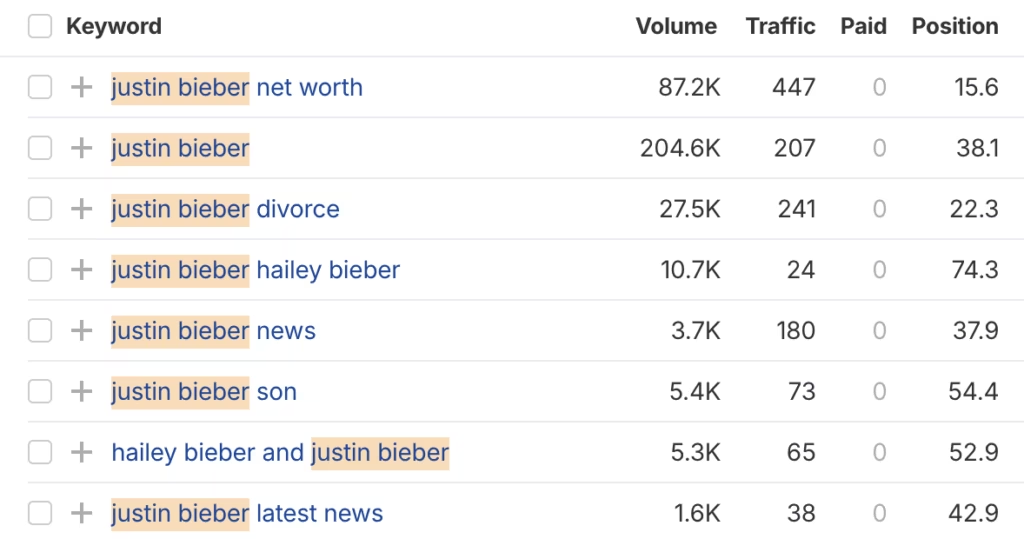
2. Ranking keywords
If a site ranks heavily for celebrity gossip or net worth buzzwords like “Taylor Swift boyfriend” or “Drake Net Worth”, or other generic one-off keyword queries, it’s likely a link farm.
🤔 Why it matters
While these keywords pull big search volumes, they lack real value and aren’t monetizable, as genuine businesses don’t focus on this kind of content.
👀 What link farms do
By exploiting such keywords, they build fake traffic signals and “ranking noise” to appear credible to SEO tools and buyers.
🔍 How to check
In Ahrefs, open the Organic Keywords report and sort by top traffic-driving keywords.
Look out for celebrity bios, year-specific queries, zero-intent or non-commercial terms, and repetitive titles/slugs like "justin bieber net worth".
3. Outbound vs. inbound links
Genuine websites strive for a balance between inbound and outbound links.
Link farms, on the other hand, are loaded with hundreds or thousands of outbound links but have very few quality backlinks — and the few inbound links they do get usually come from suspicious sources.
🤔 Why it matters
The outbound link imbalance in backlink farms is just a money grab. “Guest posts” pack unrelated paid links across niches, with no backlinks coming back.
👀 What link farms do
Link farms exist to sell links and shift PageRank — not to build lasting brands or audiences.
🔍 How to check
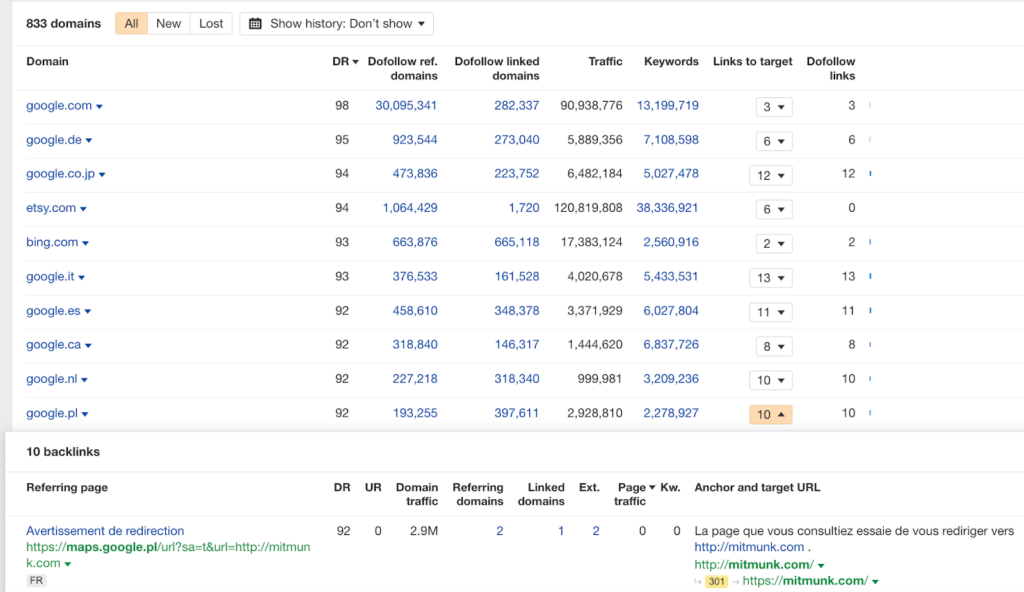
In Ahrefs, review Referring Domains to count inbound links.
Then check Outgoing Links → Linked Domains for outbound links and assess if those domains have low DR or seem suspicious.
A site with 50 inbound and 400+ outbound domains is likely a link farm or paid guest post network.
4. Domain rating
If a site’s organic traffic is stagnant, it’s not ranking for relevant keywords, and its backlinks come from low-authority or irrelevant domains, but it still has a high DR — it’s likely a link farm.
🤔 Why it matters
DR tracks backlink strength, not quality or site authority, which link farms manipulate by acquiring expired domains with strong backlinks or funneling links through PBNs.
👀 What link farms do
A high DR gives the illusion of strong authority, making it easier to sell backlinks at premium prices. Plus, it’s a prime way to manipulate search rankings indirectly by passing PageRank through artificially inflated sites.
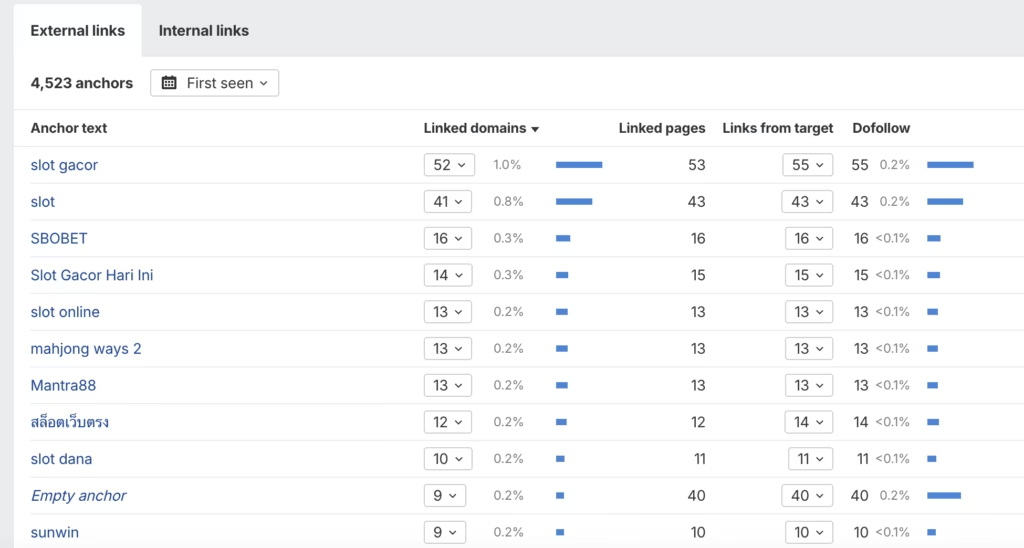
5. Outbound anchors
When reviewing a site’s external links, check the anchor texts. Suspicious sites often use trashy anchors like “best online slots,” “crypto bonus,” or “fast loans” — typical of shady niches.
🤔 Why it matters
Even commercial blogs with real authority rarely link out to gambling, payday loans, adult content, crypto betting, drug-related, VPN, or hacking software pages.
👀 What link farms do
Link farms profit handsomely by selling links to “gray” industries that rely on SEO due to Google Ads bans.
6. Backlink profile
The site might boast hundreds or even thousands of referring domains — but hardly any are strong, relevant, or reputable.
🤔 Why it matters
It’s quality, not quantity. A hundred weak blogs linking to each other won’t grow authority like one link from Forbes or TechCrunch.
👀 What link farms do
This is how they monetize authority metrics: selling guest post slots, offering link packages on Fiverr, and capitalizing on SEOs chasing “link juice” without checking quality.
🔍 How to check
Sort Referring Domains by DR in Ahrefs. If most are low (0–30) and appear spammy or irrelevant, it signals a poor-quality link profile.
7. Presence in AIO/Search Results
When you Google a topic, check if the domain appears in the AI Overview — either in the snippet or citations. If it’s missing, it might lack authority.
🤔 Why it matters
AI Overviews rarely source from low-quality or spammy sites. Even indirect mentions there signal the domain avoids thin content, poor E-E-A-T, and shady SEO tactics.
👀 What link farms do
Luckily, link farms haven’t cracked the code to appear in AI search snippets or citations — yet.
8. Keyword cannibalization
The site publishes multiple pages with the same keyword target, just changing the headline wording, like “Best CRM tools for startups in 2025” or “Top CRMs for startup founders this year.”
🤔 Why it matters
When different websites target the same keyword with minor tweaks, Google marks it as low-quality duplication, hurting authority.
🔍 How to check
Try searching: site:domain.com "keyword".
Multiple matching articles for one keyword? You've spotted a keyword cannibalization pattern!
Link Farm Alternative That Works
If you’re banking on link farms to cut costs, you’re in for a rude awakening.
At first, those link farm deals seem like a steal. But look closer — some cost just as much as legit backlinks. And when Google catches on (which it will), every site in the mix gets hit.
So really, you’re paying for problems.
If you’re going to spend, spend smarter — choose a professional link-building service like Editorial.Link.
For $1,750, you get 5 backlinks from real, traffic-driven sites, sourced through lasting relationships with site owners or genuine outreach — not from link farms built just to sell links.
Final Words
Now that you know how to spot a link farm, hopefully you also see — they’re not just pricey, they’re SEO poison.
A better choice is partnering with professional link-building services. They invest in outreach, relationships, and quality — and what you pay reflects that.
Backlink agencies like Editorial.Link focus on high-authority, traffic-driven sites. No spam, no risk — just sustainable SEO results.

